Up and Running—First Room-Temperature Quantum Accelerator of Its Kind in Europe
June 05 2025 -- Fraunhofer IAF’s unique quantum computing infrastructure operates the latest quantum accelerator by Quantum Brilliance. It is Europe’s first compact quantum accelerator based on nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamond. With its compact size and robust integration without cryogenics, the second-generation Quantum Development Kit (QB-QDK2.0) enables hybrid quantum-classical computing. The system will be made available to partners across science and industry to explore its capabilities and advance real-world quantum applications.
To further accelerate its pioneering research in the field of quantum computing, the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF is expanding its unique quantum computing infrastructure with the latest system from Quantum Brilliance (QB).
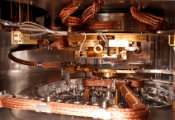
Following a public tender, the Quantum Development Kit (QB-QDK2.0) is operational and integrated directly into the high-performance computing infrastructure at Fraunhofer IAF. The system requires no cryogenics, fits into a standard 19” server rack, and enables energy-efficient, hybrid quantum-classical computing in conventional IT environments. “This is likely the first time anyone has asked ‘What should we do with the leftover space in the rack?’ when installing a quantum computer,” said Prof. Rüdiger Quay, Director at Fraunhofer IAF. “The QB-QDK2.0 fits seamlessly into our existing HPC environment. Paired with the open-source Qristal SDK and Emulator, we have a fully integrated platform for quantum research, spanning from algorithm development to advanced hardware.”
Compact and robust design
The QB-QDK2.0 is a compute node that integrates quantum processing units (QPUs) with classical co-processors, including NVIDIA GPUs and CPUs, in a single, compact module. This proximity enables efficient implementation of hybrid quantum-classical algorithms, especially in fields like quantum machine learning where classical and quantum neural networks converge.
“With the installation and go live of our QB-QDK2.0 at Fraunhofer IAF, QB have set the foundation for customers to begin working with NV based quantum computing. I would like to thank everyone involved for their hard work and dedication in making this project a success. This development opens new possibilities for advanced research and applications in quantum computing, and we are excited to continue working with the wider community in Germany and Europe and exploring new opportunities in this field,” states Quantum Brilliance Chief Revenue Officer Mark Mattingley-Scott.
The installation of the new system was supported by SVA System Vertrieb Alexander GmbH. With their extensive project expertise in high-quality IT products the QB-QDK2.0 was set up in May 2025.
Quantum computing based on diamond
Quantum Brilliance’s technology uses synthetic diamond substrates, in which individual nitrogen atoms are placed within the atomic carbon lattices, creating NV centers which function as qubits. Computers based on NV centers in diamond offer several advantages: They have long coherence times, allowing quantum information to be stored over extended periods. Additionally, they are resilient to environmental noise and other external influences, making them an ideal platform for stable quantum operations and industrial applications even at room temperature.
To make the potential of quantum computing tangible today, the quantum computing application laboratory of Fraunhofer IAF provides practical access to diamond-based quantum computers that utilizes NV centers. Alongside the new system of Quantum Brilliance, the application laboratory also features a NV-based quantum system developed by the University of Stuttgart. Inspired by these systems, Fraunhofer IAF is developing its own diamond-based quantum computer.
The quantum computing infrastructure at Fraunhofer IAF enables industry and research professionals to explore the capabilities of NV center-based technology, optimize quantum algorithms, and tackle real-world computational problems.
After a test phase, the QB-QDK2.0 will be made accessible to partners of Fraunhofer IAF from science and industry and thus improves the unique quantum computing ecosystem in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The acquisition of the system is in line with the quantum computing roadmap of QuantumBW, the state’s innovation initiative for quantum technologies. With QuantumBW, Baden-Württemberg actively promotes quantum sciences, especially based on diamond hardware, and positions itself globally at the cutting edge of quantum technology research and development.