SoftBank Corp. to Enhance Communications Performance by Optimizing Radio Base Station Settings With Quantum Computing Technology
July 29, 2025 - SoftBank Corp. (“SoftBank”) conducted a proof-of-concept experiment in Tokyo using an Ising machine, a type of quantum computing technology, to optimize radio base station settings. As a result, in 5G communications using carrier aggregation (“CA”), SoftBank successfully improved downlink data speed by approximately 10% and increased data transmission capacity by up to 50% compared to conventional settings.
In this proof-of-concept experiment, SoftBank aimed to expand the coverage area of CA by optimizing base station settings using quantum computing technology. CA is a technology that enables high-speed, stable communication by simultaneously utilizing multiple frequency bands. To function, it requires predefined associations between base stations, referred to as “CA links.” However, as the number of base stations increases, determining the optimal CA link configuration becomes exponentially more complex. For instance, selecting pairs from 10 base stations yields 45 combinations. Since each pair can either be linked or not, the total number of possible CA link patterns reaches 35 trillion (2 to the power of 45). Moreover, constraints such as the maximum number of CA links assignable to each base station further complicate the task, making it extremely difficult to identify the optimal combination that maximizes CA-enabled area coverage.
In the proof-of-concept experiment, an area of Tokyo with multiple 5G base stations was divided into a fine-grained mesh. Meshes that could simultaneously receive signals at different frequencies from multiple base stations were identified as location candidates for CA deployment. Based on this mesh information, the optimal combination of CA links to maximize the number of CA-capable meshes was computed using quantum computing technology (see Figure 1). To perform this computation, the problem was formulated as a mathematical optimization problem and solved using an Ising machine, which is specifically designed to perform computations specialized for combinatorial optimization.
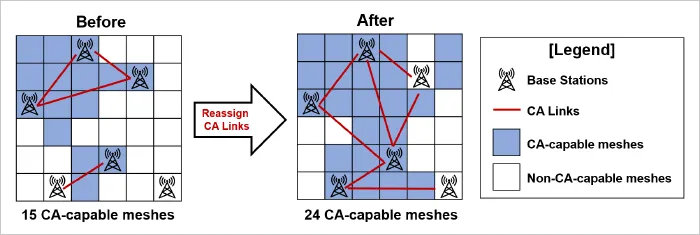
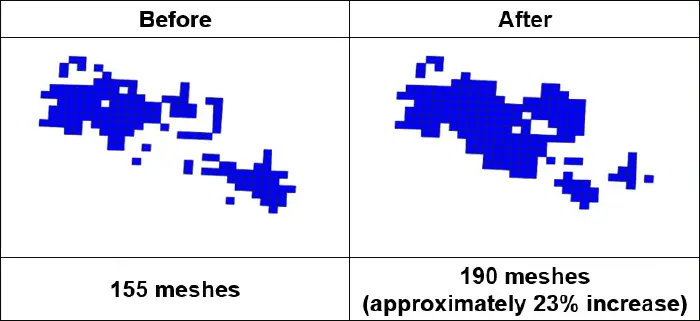
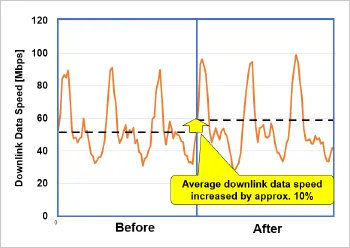
Based on the results of the optimization, a CA link configuration was generated and used to simulate the CA-capable coverage area. The simulation confirmed that CA could be made available over a broader area compared to conventional configurations (see Figure 2). When this configuration was applied to 5G base stations operating in a specific area of Tokyo, the CA coverage area expanded, and the average downlink data speed improved by approximately 10% (see Figure 3). In addition, both the CA utilization ratio (the proportion of connections utilizing CA), and the amount of data transmitted via secondary cells increased by up to 50% (see Figure 4). These results demonstrate that optimizing base station settings using an Ising machine enables more efficient utilization of the radio spectrum and leads to improved communication performance. This technology contributes to delivering a more seamless user experience, such as smoother high-resolution video streaming and online gaming.
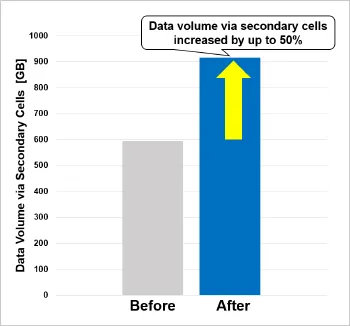
(Total data volume for secondary cells before and after applying the optimized CA configuration)
Going forward, SoftBank will consider applying quantum computing technologies not only to network architecture optimization, but also to operational enhancements, aiming to expand these initiatives across a broader range of services and deliver even more seamless and high quality services.